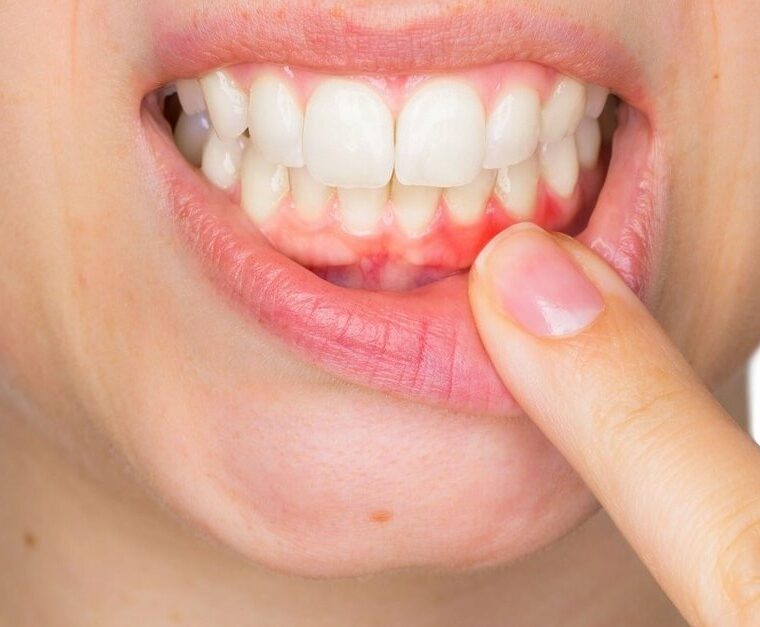
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by the irritation from dental plaque buildup on the teeth. It is the earliest and mildest form of gum disease, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial to prevent progression to more severe periodontal conditions. Effective and regular oral hygiene, including thorough tooth brushing, is essential for prevention. If symptoms such as gum swelling, bleeding during brushing, or bad breath appear, prompt consultation with a dentist is recommended.
Gingivitis develops primarily due to inadequate oral hygiene. Other contributing factors include infections related to systemic illnesses and malnutrition. It is a bacterial infection and can cause pain depending on the severity of the inflammation. When detected early, gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral care, but neglecting treatment may lead to serious complications.
What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
Early stages of gingivitis often show no symptoms and can go unnoticed. As the condition advances, typical symptoms include:
- Gum recession,
- Bleeding during tooth brushing,
- Swelling, redness, and tenderness of the gums,
- Pain while chewing or speaking,
- Sensitivity to hot or cold stimuli,
- Persistent bad breath,
- Loose teeth,
- White patches or inflammation on the gums.
What causes gingivitis?
Gingivitis results from the accumulation of bacterial plaque in the pockets between the teeth and gums when food residues are not properly cleaned. This plaque irritates and inflames the gums. While bacterial plaque is the primary cause, other factors include:
- Smoking,
- Pregnancy,
- Certain systemic diseases,
- Diabetes,
- Genetic predisposition,
- Use of medications affecting the gums,
- Structural problems in teeth,
- Old or damaged dental fillings requiring replacement.